The gut microbiota is involved in the lung’s defense against viral respiratory infections
The microbiota plays a key role in the development, education and function of the immune system, both locally and systemically. While the airway microbiota locally regulates immune function, the gut microbiota can also influence respiratory immunity, via the gut-lung axis.1 Alteration of the lung and gut microbiota has been observed in many respiratory diseases, however whether the dysbiosis at these sites is a cause or a consequence of disease remains to be determined.2 Alteration of gut microbiota composition, through either diet, antibiotic use, aging, or disease, is associated with altered immune responses and homeostasis in the airways,3 highlighting that the gut microbiota can influence disease development throughout the body, including the risk of respiratory infections (Fig 6).4
Lay public section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
Sections

About this article
In comparison to the gut microbiota, studies on the lung microbiota are still in their infancy.5 The lung was originally thought to be sterile but recently, researchers have discovered that the lung harbours its own microbiota, with a composition distinct from the gut microbiota.6
Any factors inducing microbiota dysbiosis can alter the beneficial gut-lung cross-talk, increasing susceptibility to respiratory infections.10
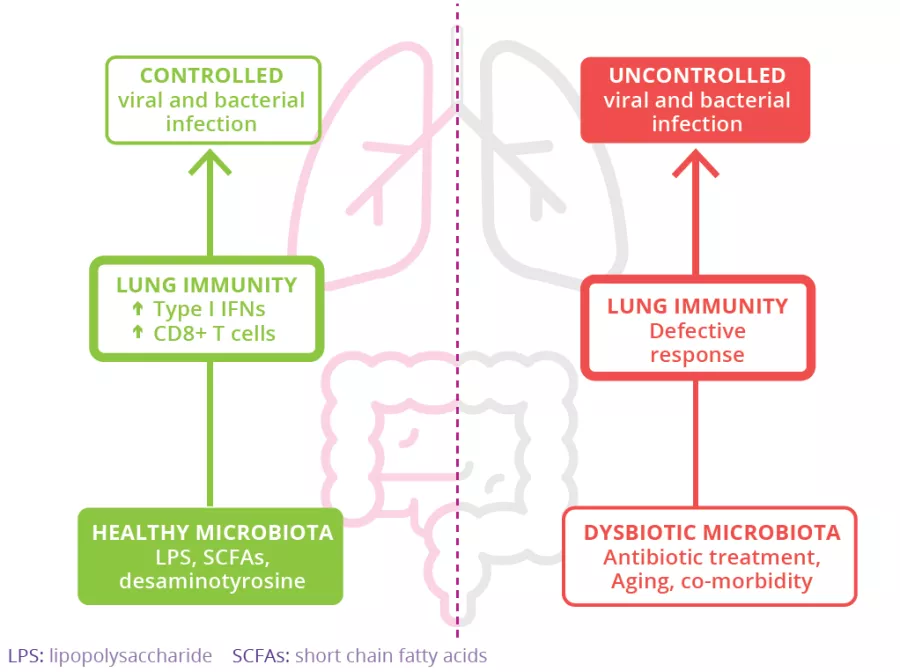
Studies have shown that gut microbiota may be involved in providing protection against viral respiratory infections (such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus),2 via numerous mechanisms. For example, gut microbial metabolites such as SCFAs (obtained from dietary fiber fermentation by commensal bacteria) and desaminotyrosine (a degradation product of plant flavonoids produced by human gut bacteria)7 influence the lung production of Type I interferon (IFNs) which elicit anti-viral protection. 8,9 Along with microbial metabolites, microbial components (such as LPS) help arm the lungs against viral respiratory infections (Fig 6). The gut microbiota also plays a role in viral (influenza) clearance by stimulating CD8+ T-cell effector function.10
FIGURE 6: The role of the gut microbiota in viral respiratory infections.
Adapted from Sencio V et al, 202010
Any factors inducing gut microbiota dysbiosis (aging, antibiotics, diseases such as obesity, diabetes…) can also alter the normally beneficial gut-lung cross-talk, increasing susceptibility to respiratory infections.10