What to take away? Intestinal Immunity
Lay public section
Find here your dedicated section
Sources
This article is based on scientific information
Sections
About this article
The microbiota plays critical roles in the development and education of the host’s innate and adaptive immune system components, while the immune system orchestrates the maintenance of key features of host-microbe symbiosis. Maintaining homeostasis between the gut microbiota and the immune system is essential, determinants interfering with neonatal gut establishment (antibiotics...) may potentially lead to negative health outcomes.1
80% At least 80% of the body Ig-producing cells are located in the gut (2)
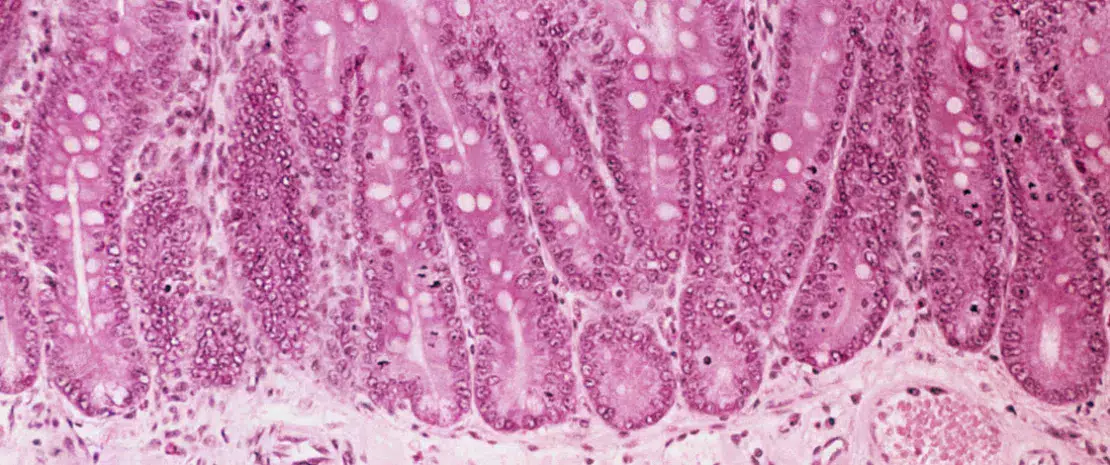
MUCUS
The intestinal mucus layer is at the crucial interface between host and gut microbiota. Its disruption leads increased penetration or passage of potentially harmful bacteria that can eventually cause inflammation and infection.3
2 Brandtzaeg P. (2017) Role of the Intestinal Immune System in Health. In: Baumgart D. (eds) Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Springer, Cham.